-- Pest Library --
Vole
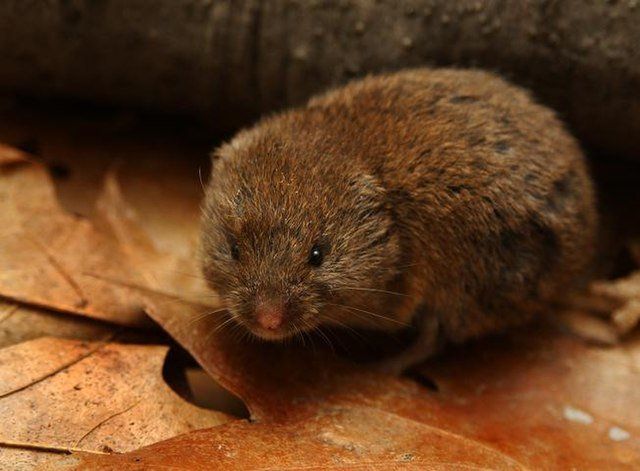
Vole Description
Voles resemble mice in appearance and are often mistaken as mice. Voles are compact rodents with stocky bodies, short legs, and short tails. Their eyes are small and their ears partially hidden. They usually are brown or gray, though many color variations exist. The adult vole ranges from 3.5 to 5 inches in length and weighs 1 to 2.5 ounces.
Diet
Voles are vegetarians and can cause severe feeding damage to seedling and turf grass. The stems and leaves of grasses comprise the majority of their diet, but they will also consume other green vegetation and fruits. Voles do not hibernate and are active throughout the year. During severe winters and snow cover, when green vegetation is scarce, voles often girdle tree trunks and roots killing or damaging trees and shrubs.
Life Cycle & Reproduction
Voles can produce from 5 to 10 litters per year, with an average of 5 young per litter. Gestation is about 21 days, and females can mate again the day after her young are born. Young voles grow quickly, are weaned at 2 to 3 weeks, and are sexually mature in a month or two. Voles can live up to two years. Just one single female vole can produce 75 or more offspring in a single year. Assuming that her offspring also mated and reproduced – several thousand voles could result from that one female vole during a one year time period.
Habitat
Voles live in areas of heavy grass and weed cover. They use both above-ground runways and underground tunnels to move from place to place. The surface runway openings are 1 1/2 to 2 inches wide. The surface runway system will have numerous openings into underground tunnels below the surface. Vole nest sites are often beneath the protection of object lying on the ground. Burrow openings are often located next to these protective objects such as rocks, rock walls, cement patios and/or walkways. The burrow openings may also be beneath protective cover such as vegetation or shrubbery. Occasionally, the burrow openings are located in the open spaces such as lawn turf. Voles may be active day or night, but most activity occurs at dawn and dusk. Their activity is comprised of short, quick visits from the burrow through their runways and back.
Threat
Voles can prove destructive to turf lawns and young trees and plants. Voles also feed regularly on bark and have been known to kill saplings. Unlike most rodents, voles are active day and night. They reproduce quickly, leading to serious infestations and damage if left unchecked.